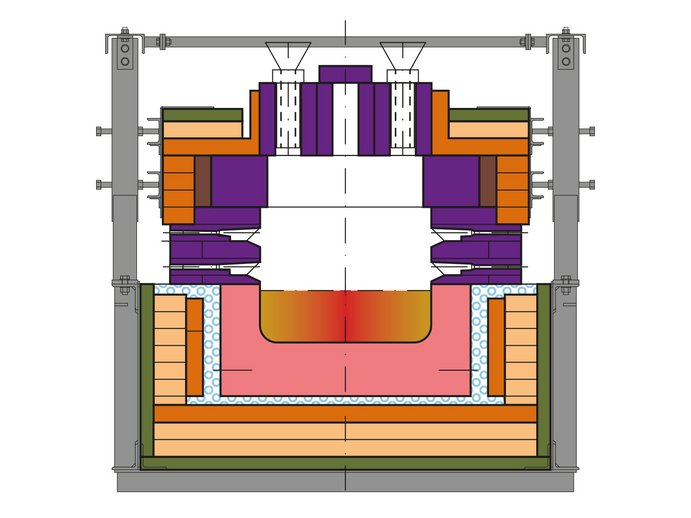
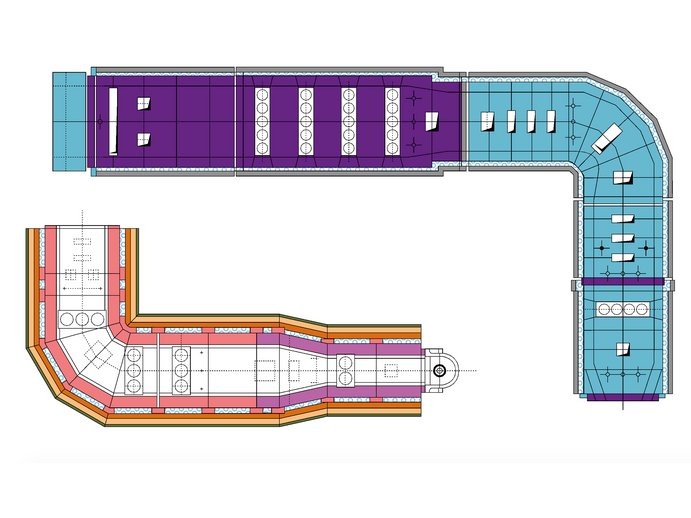
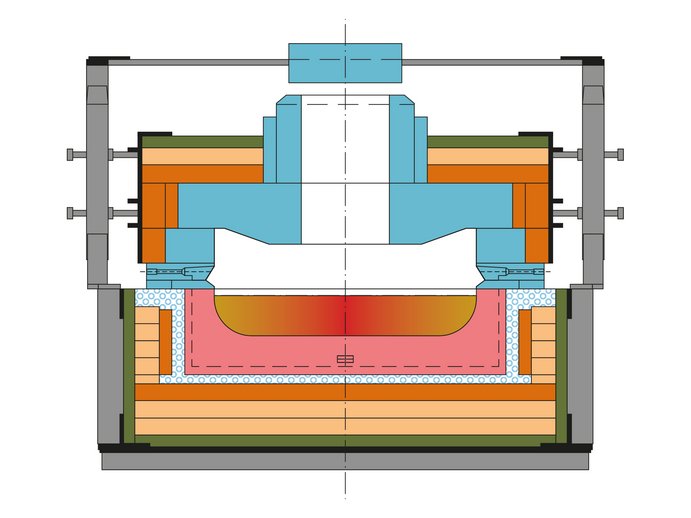
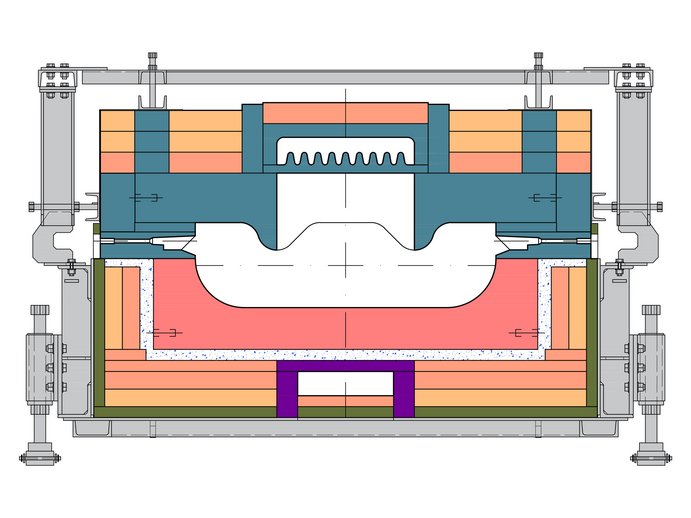
A colouring forehearth is a favourable method for the production of coloured glass without having to change the colour in the entire furnace. The advantages are having two colours simultaneously and the possibility of a temporary colouring process. Thus, the flexibility of the glass melting furnace can be increased and several different colours can be produced from one furnace.
For many years HORN® has successfully designed colouring forehearths according to the specific requirements of glass manufacturers.
Many colouring forehearths for varying glass applications such as container glass, tableware or sheet glass have been installed worldwide. All colouring forehearths can be provided together with refractory material, combustion system and control equipment.
Colouring agents (colouring product) are used for the colouring process. Copper, chrome, nickel, selenium, cobalt and other elements can be used to produce a wide range of colours. Various combinations of these elements enable an even larger palette of colours.
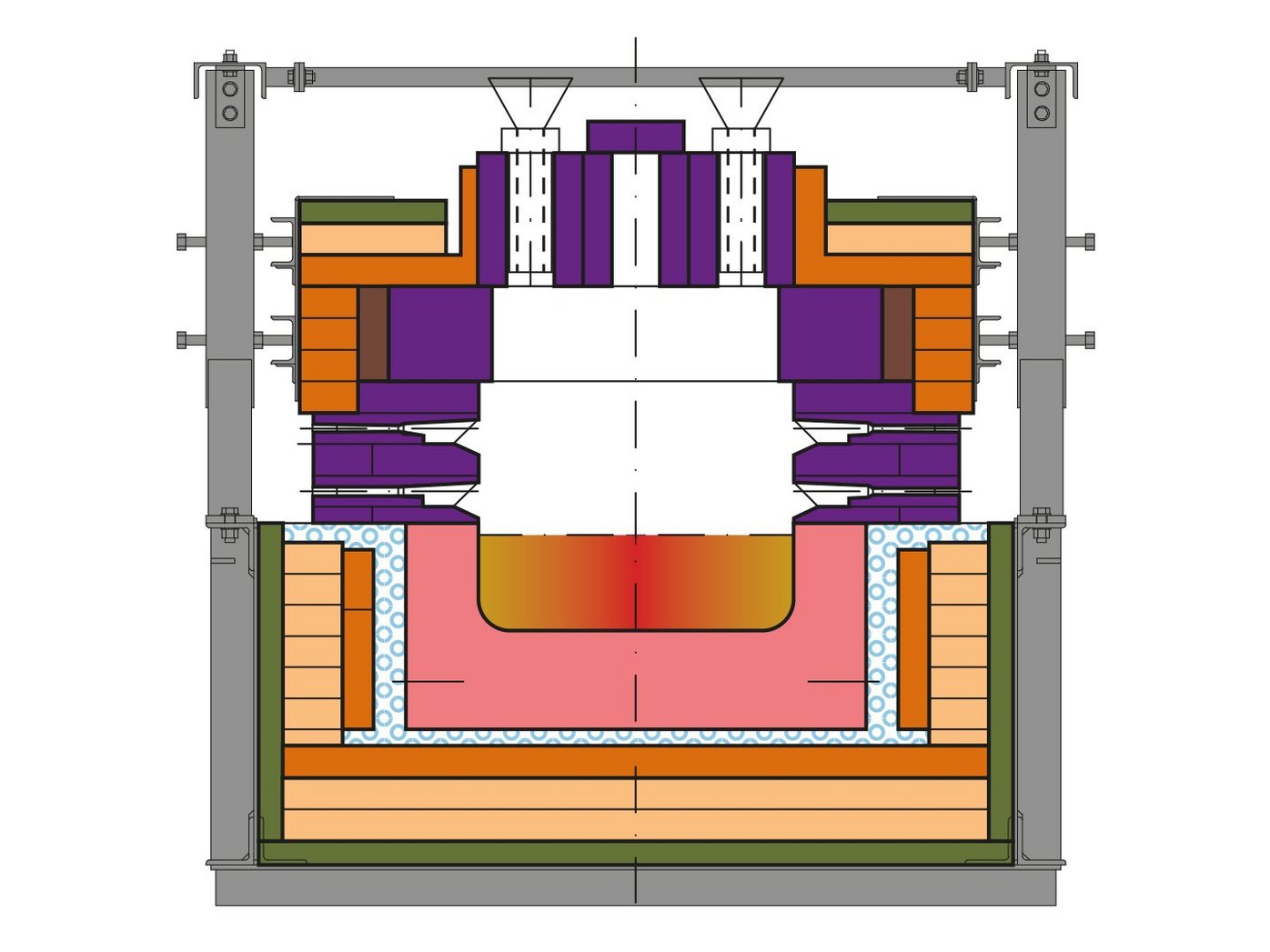
All forehearths are individually designed depending on the colours required, the tonnage and the conditions on-site. All forehearths generally consist of a heating-up zone, a melting zone, a stirrer zone, a cooling zone and an equalising zone.
HORN® forehearths can process various types of glass, e.g. cosmetics glass, crystal glass, tableware, container glass and figured glass.
There is a wide range of colours that can be used in forehearths, such as black, grey, smoke, blue, purple, violet, pink, bordeaux or green, including different types of green such as antique green, emerald green or dead leaf green.
The channel blocks in the heating-up, melting and stirrer zones are usually made of fused cast AZS (Aluminium-Zircon-Silicate). Cooling and equalising section channels can be provided as fused cast AZS, alpha / beta alumina or bonded zircon mullite.
Superstructure material in the heating-up and stirrer zone is made of special bonded alumo-zirconoxide refractory material (zircon mullite) with high density and low porosity in order to reduce corrosion due to the high temperature and aggressive evaporations from the colouring agent. The refractory superstructure in the cooling and equalising zones features a special design for optimal cooling and heating efficiency and is made of high alumina materials. Ultramodern insulation materials are used for all zones to achieve extremely low heat loss values in order to reduce fuel consumption and improve the thermal homogeneity of the glass.
The glass melt needs to enter the melting zone at a temperature between 1260 °C and 1320 °C. For this reason, it might be necessary to provide a heating-up zone in front of the melting zone. A dosing device and water-cooled feeding tubes are installed at the start in order to feed the colouring agents onto the glass surface. The combustion system is intensified by means of two burner rows at each side along the melting zone to compensate for the heat loss of the water-cooled feeding tubes.
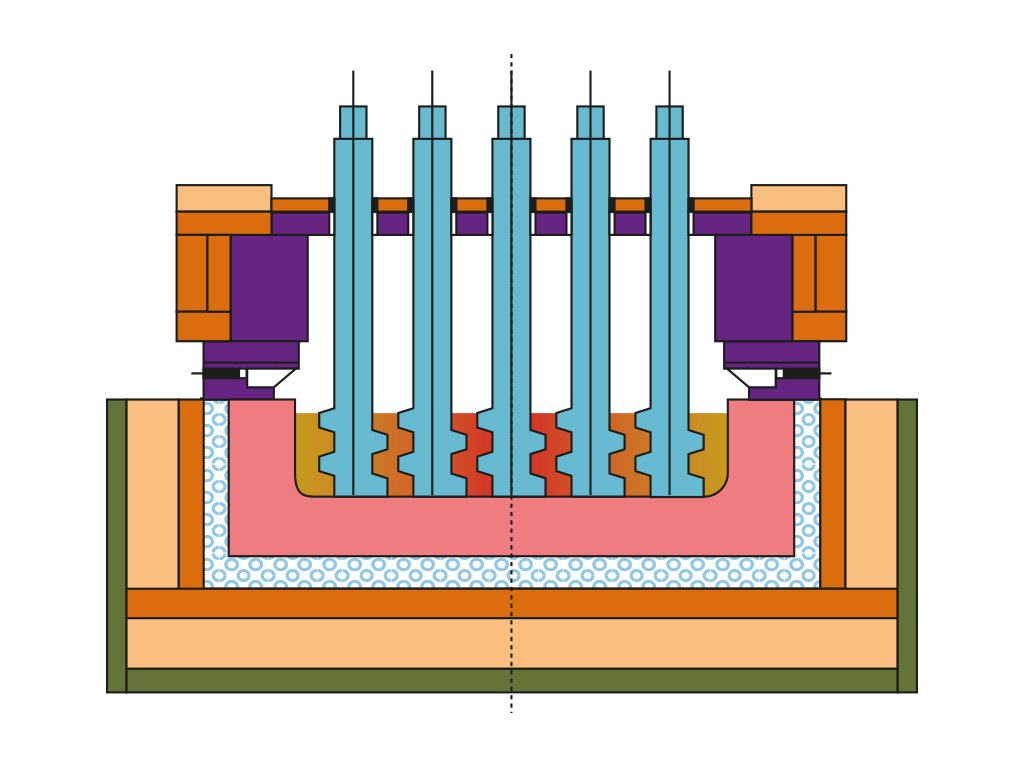
The function of the stirrer zone is to mix the molten colouring agent with flint glass. For this purpose the roof of this zone has several openings through which ceramic stirrers are installed.
The number of stirrers and stirrer rows depends on the type of colours, intended colour homogeneity, total pull and length of the forehearth. A certain amount of residence time has to be considered in this zone.
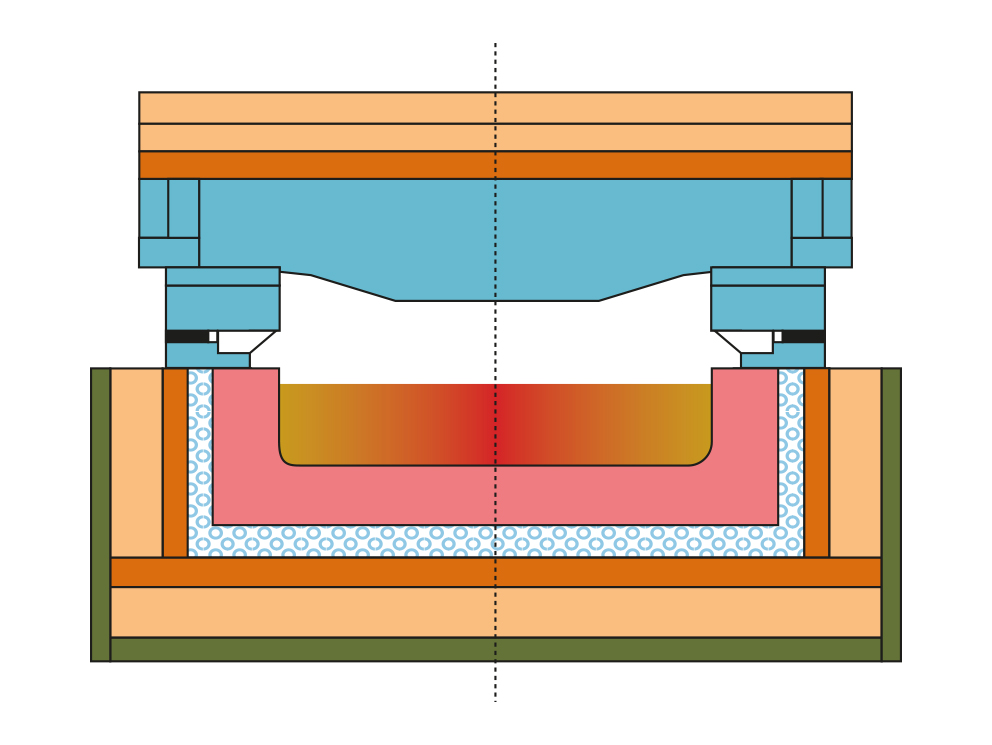
The first zone after the stirrer zone is constructed as the cooling zone. Due to the higher temperature required for melting and stirring, the glass has to be cooled and conditioned for the forming process. Cooling facilities such as radiation openings and/or cooling air channels in the roof are applied according to the type of forehearth such as the GCS® Series 200 or 301-advanced. Cooling zones are designed individually depending on the articles being produced and the type of colouring agents.
The equalising zone, which is part of the colouring forehearth, ensures the final conditioning for the forming process. An additional stirring system is advantageous for temperature homogeneity. The openings in the superstructure for the stirrers are planned during engineering.
Frits of colouring concentrate (colouring products) are used for the colouring process. Copper, chrome, nickel, selenium, cobalt and other elements can be used to produce an entire range of colours.
A stirrer unit consists of several stirrers, coupler bearings and a chain drive as well as cooling equipment for drives and couplers.
The lambda control is an optional tool which ensures constant oxygen content in the gas/air mixture.
COOKIES
We use cookies to make it easier to use and to further improve our service.
If you have given us your consent, you can revoke it at any time in the data protection declaration.
COOKIES
Necessary
Necessary cookies help make a website usable by enabling basic functions such as page navigation and access to secure areas of the website. The website cannot function properly without these cookies.
C3 Cookie
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c3kie | hornglass.com | Saves the consent status of the user whether the cookie window should be displayed. | 180 days | HTTP Cookie |
Technical
Technichal cookies help to improve the user experience of the website. New functionalities will be enabled.
YouTube
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| yt-player-headers-readable | YouTube | Used to determine the optimal video quality based on the visitor's device and network settings. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | YouTube | Tries to estimate the range of users on pages with built-in YouTube videos. | 179 days | HTTP Cookie |
| YSC | YouTube | Registers a unique ID to keep statistics on which videos from YouTube the user has seen. | Session | HTTP Cookie |
| yt.innertube::nextId | YouTube | Registers a unique ID to keep statistics on which videos from YouTube the user has seen. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| yt.innertube::requests | YouTube | Registers a unique ID to keep statistics on which videos from YouTube the user has seen. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-cast-available | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Session | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-cast-installed | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Session | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-device-id | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Persistent | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-fast-check-period | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Session | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-session-app | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Session | HTML Local Storage |
| yt-remote-session-name | YouTube | Saves the user's video player settings with embedded YouTube video. | Session | HTML Local Storage |
Advertisement
Advertisement cookies allow our advertising partners to show you ads that fit your interests.
TikTok
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _ttp | TikTok | Used to store a unique user ID. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _fbp | Used to store and track visits to websites. | 3 months | HTTP Cookie |
Statistics
Statistics cookies help website owners understand how visitors interact with websites by collecting and reporting information anonymously.
Google Tag Manager
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _ga | Google Tag Manager | Registers a unique ID that is used to generate statistical data on how the visitor uses the website. | 2 years | HTTP Cookie |
| _ga_ | Google Tag Manager | Collects data on how often a user visited a website, as well as data on the first and last visit. Used by Google Analytics. | 2 years | HTTP Cookie |
Microsoft Clarity
| Name | Provider | Purpose | Expiration | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _clck | Microsoft | Persists the Clarity User ID and preferences, unique to that site is attributed to the same user ID. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| _clsk | Microsoft | Connects multiple page views by a user into a single Clarity session recording. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| CLID | Microsoft | Identifies the first-time Clarity saw this user on any site using Clarity. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| ANONCHK | Microsoft | Indicates whether MUID is transferred to ANID, a cookie used for advertising. Clarity doesn't use ANID and so this is always set to 0. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| MR | Microsoft | Indicates whether to refresh MUID. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| MUID | Microsoft | Identifies unique web browsers visiting Microsoft sites. These cookies are used for advertising, site analytics, and other operational purposes. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |
| SM | Microsoft | Used in synchronizing the MUID across Microsoft domains. | 1 year | HTTP Cookie |